China increases its presence in Russia’s former Central Asian backyard
- A recent joint exercise in Tajikistan is the latest example of Beijing’s growing security and economic interests in the former Soviet republic
- Analysts say Moscow may not be happy about China’s growing reach in the lawless, mountainous area and will be keeping an eye on the situation
China is increasing its military and economic presence in parts of central Asia that Russia has traditionally considered its sphere of influence – a development some analysts believe could cause concern in Moscow.
While Russia’s influence remains strong in many former Soviet republics, China is steadily building up its military and economic influence in Tajikistan, particularly in the remote, mountainous areas on its western borders where central government authority is weak.
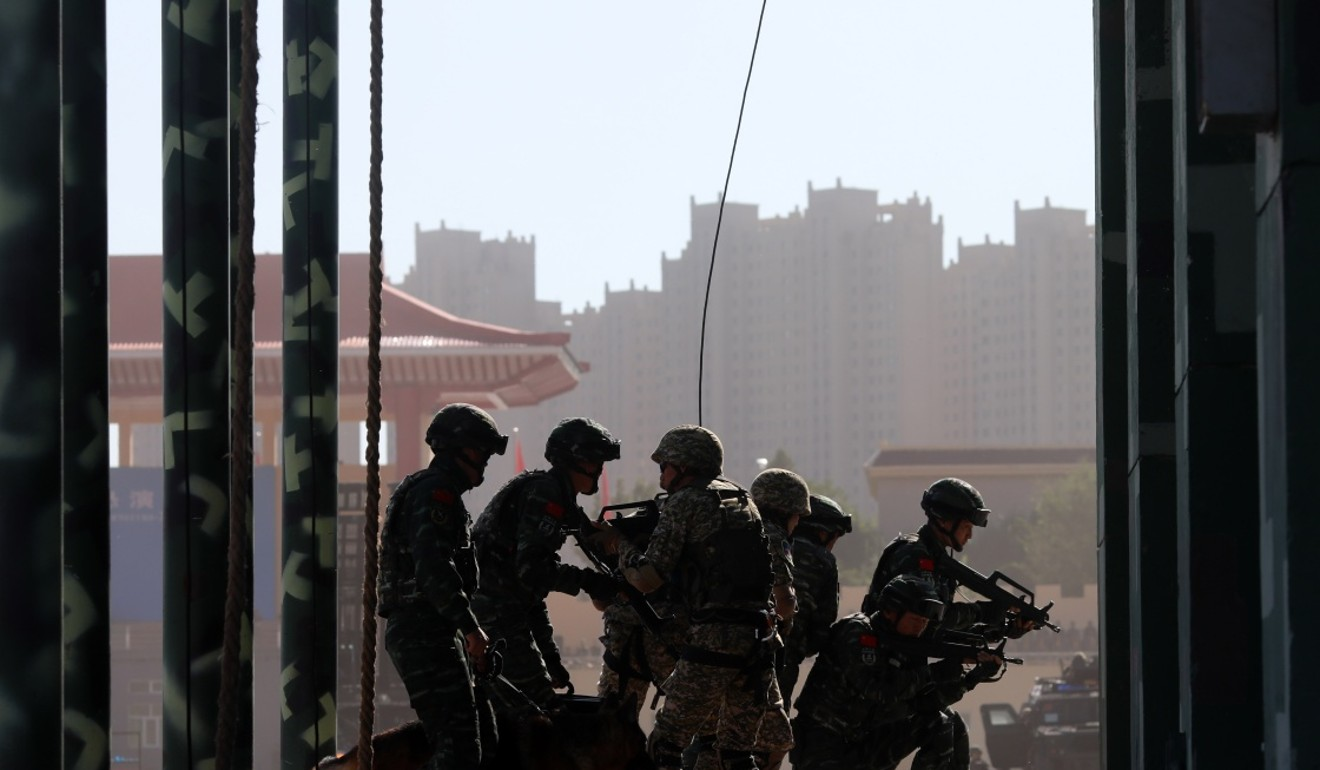
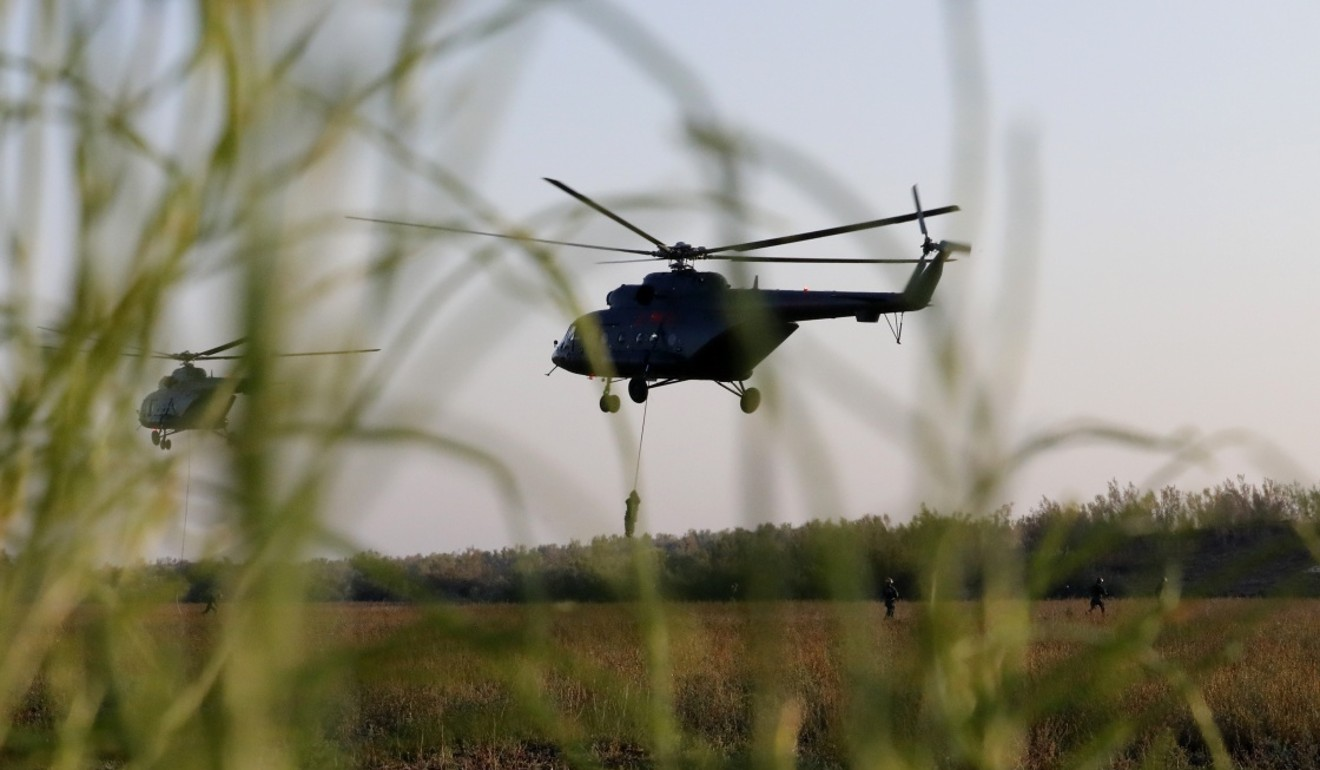
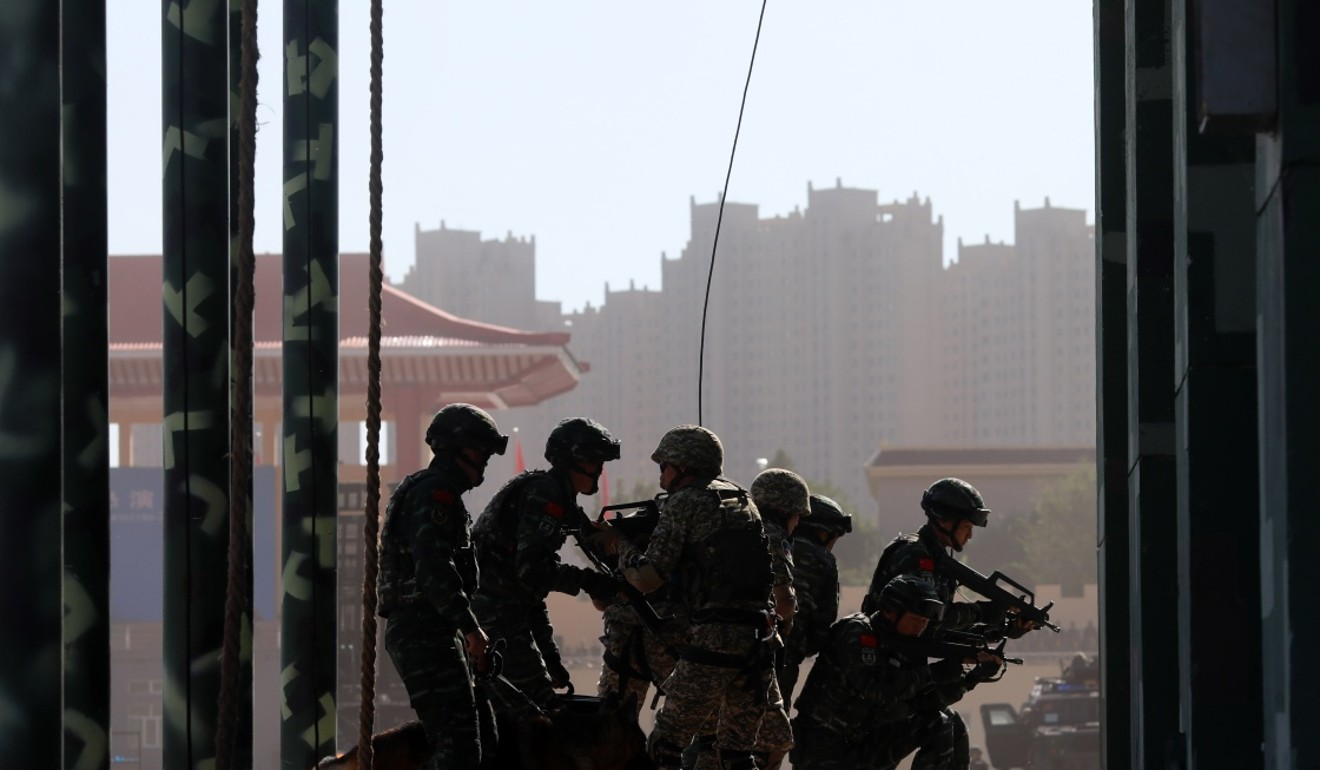
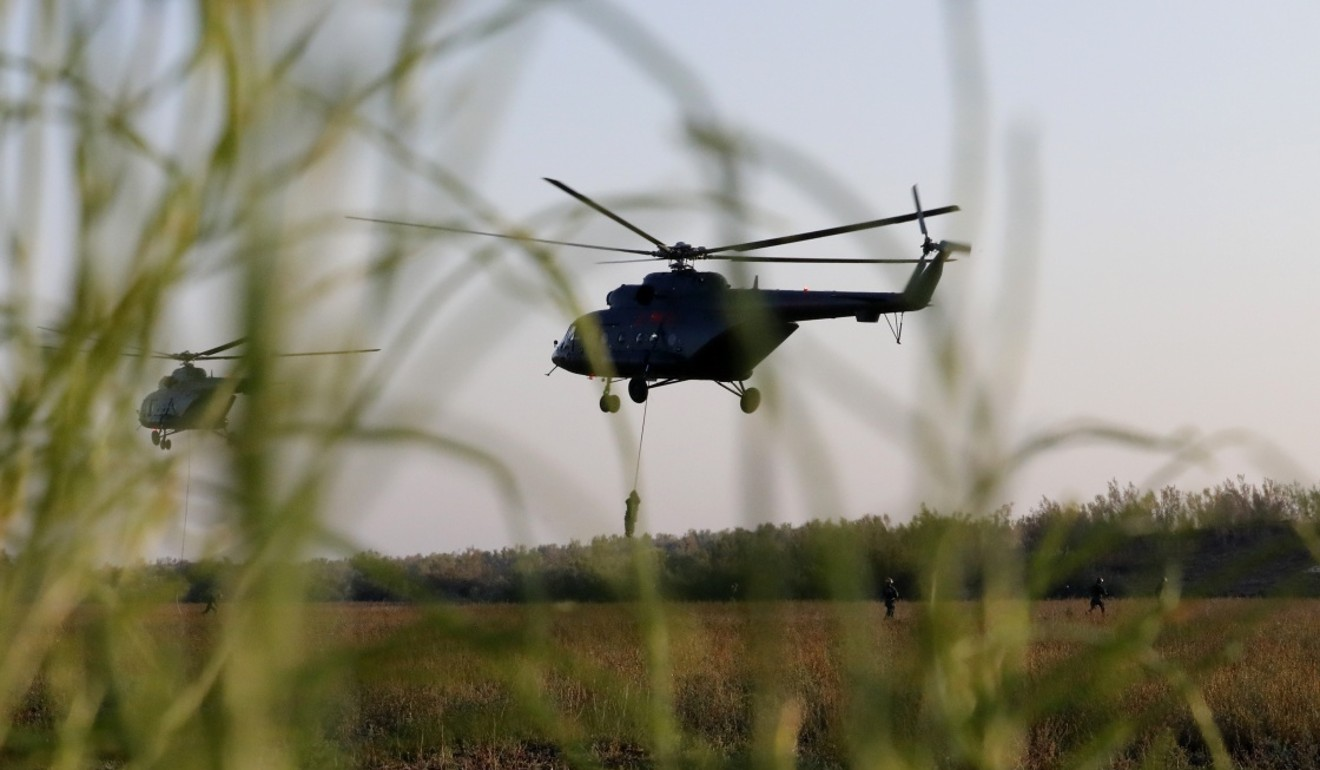
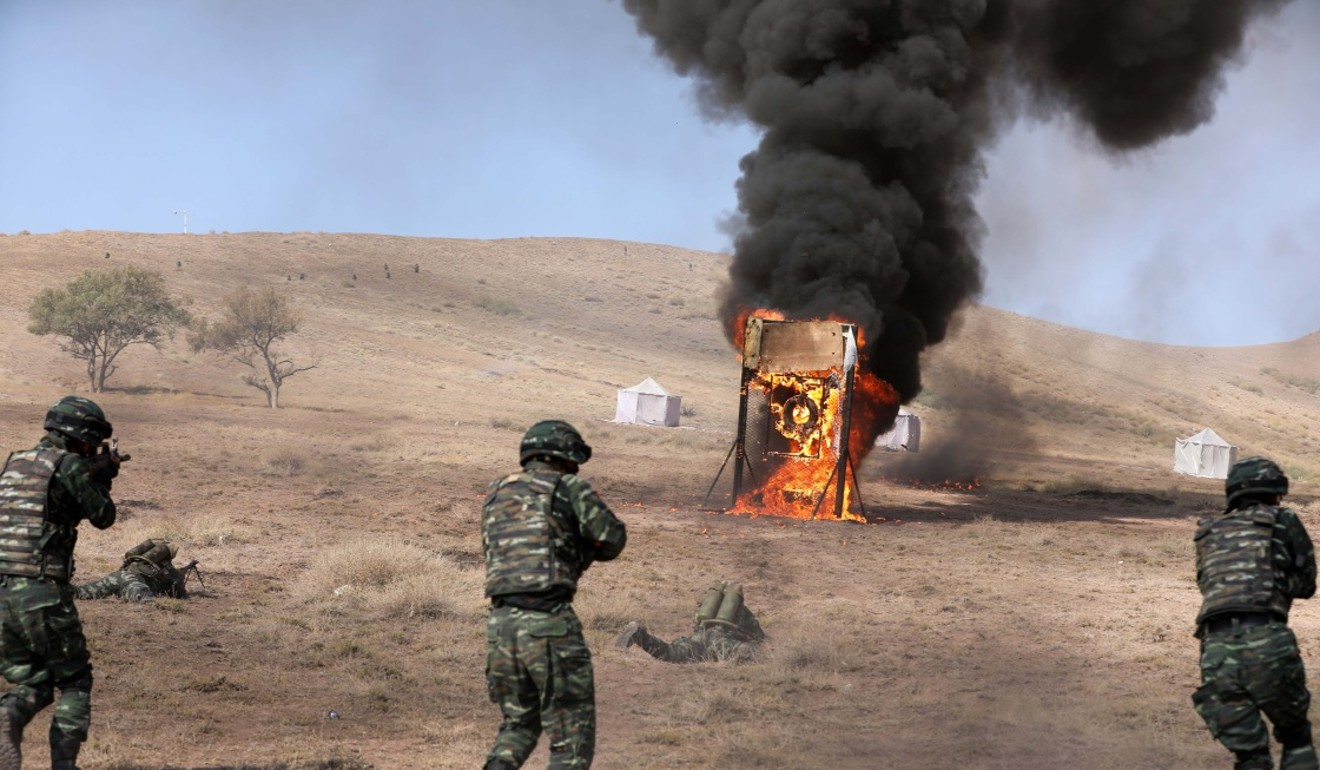
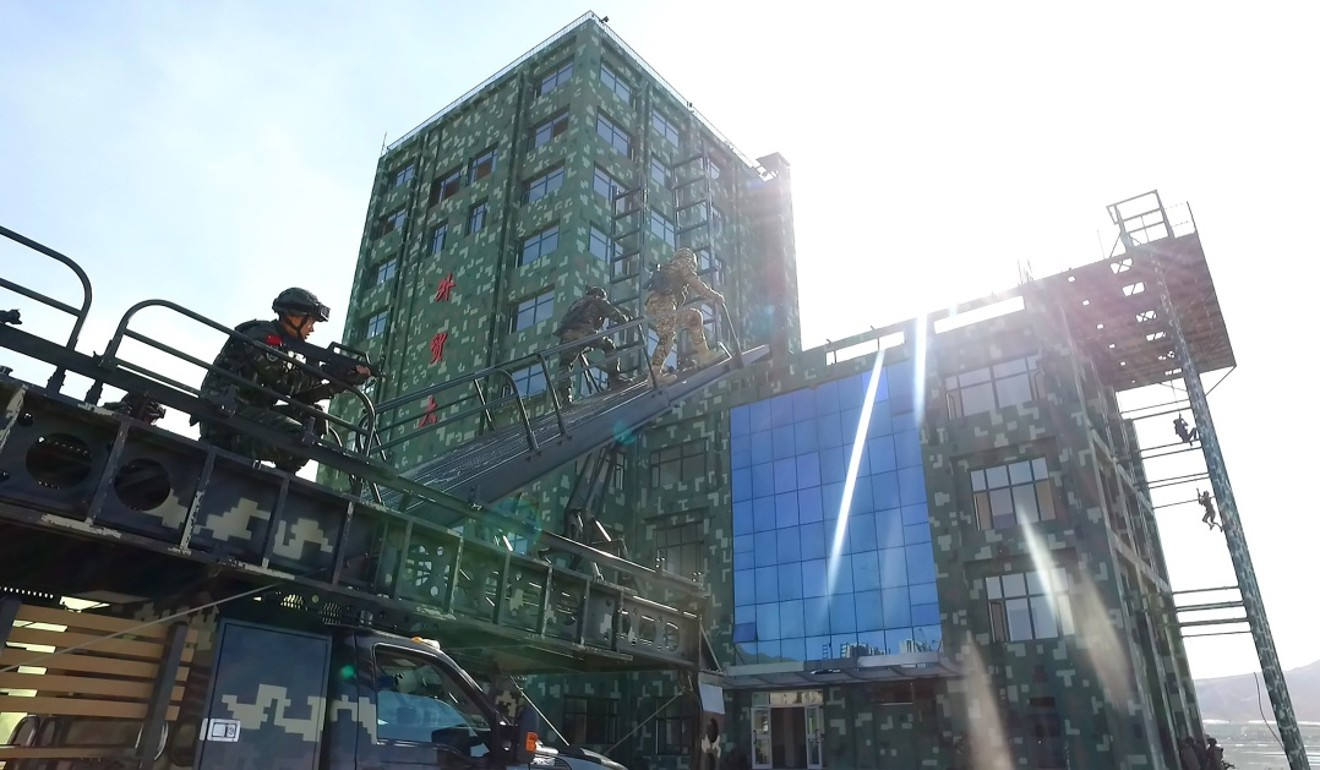
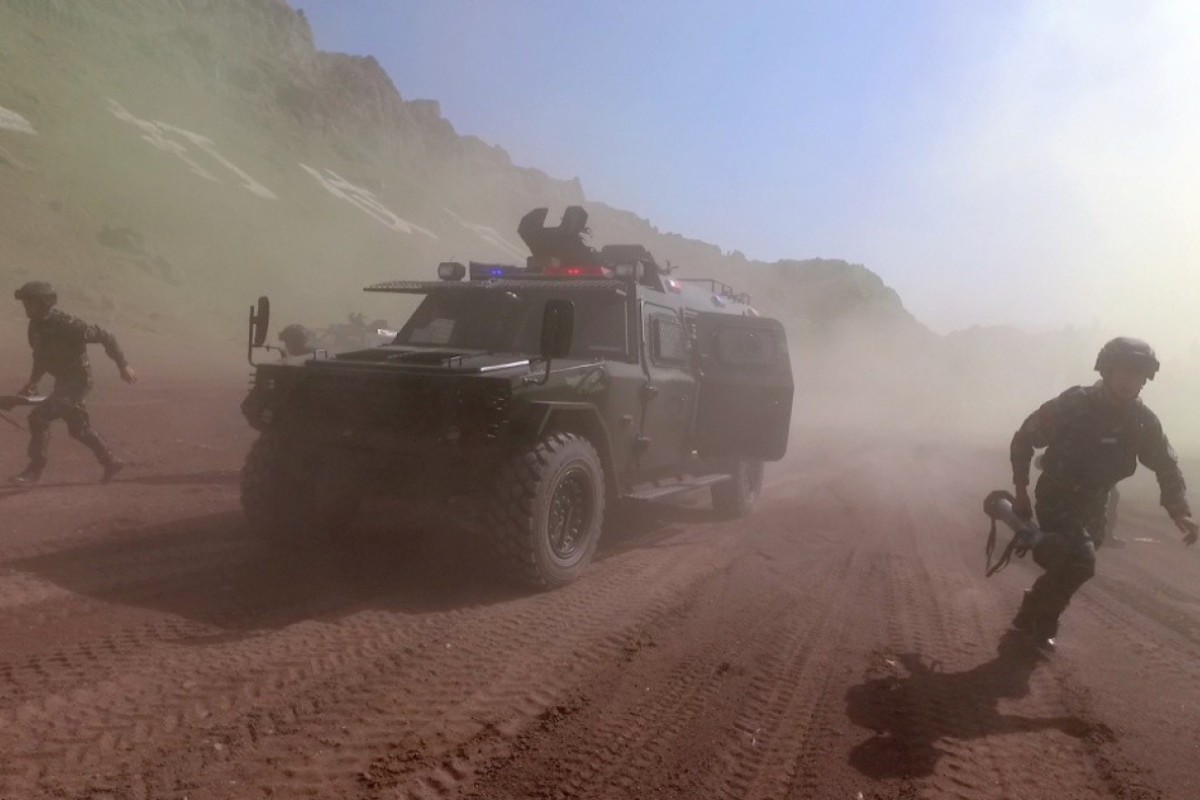
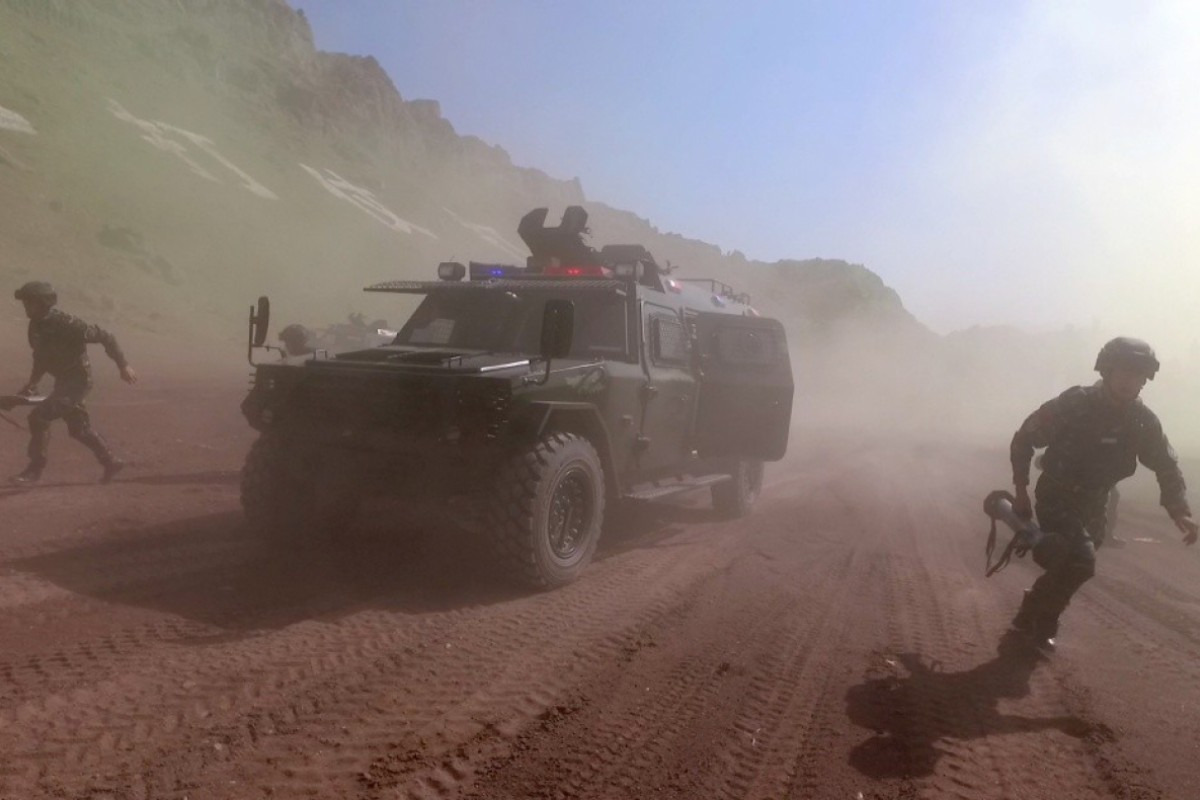
Chinese troops recently concluded a joint drill in eastern Tajikistan involving 1,200 troops from both countries.
- The eight-day exercise that finished on August 13 was conducted in the autonomous Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region, a sparsely populated territory in the high Pamir mountains, which borders China’s Xinjiang region and Afghanistan.
Although this year’s exercise involved fewer troops than the 10,000 involved in a previous drill three years ago, it tested the use of advanced aerial vehicles and ground reconnaissance technology to monitor the area.
The landlocked country is strategically important for China, which is worried that the porous borders will serve as an entry point for drugs and Islamic militants into Xinjiang, where its deradicalisation strategy has led to the detention of a million Muslim minorities in reeducation camps.
- It also sits along the trade routes China hopes to develop under the Belt and Road Initiative – Beijing’s flagship plan to expand its global influence through infrastructure, trade and investment – but the area has long been plagued by lawlessness and outbreaks of violence.
 Chinese and Tajik troops completed a joint exercise earlier this month in the mountainous region of Gorno-Badakhshan. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese and Tajik troops completed a joint exercise earlier this month in the mountainous region of Gorno-Badakhshan. Photo: XinhuaChina is increasing its military and economic presence in parts of central Asia that Russia has traditionally considered its sphere of influence – a development some analysts believe could cause concern in Moscow.
While Russia’s influence remains strong in many former Soviet republics, China is steadily building up its military and economic influence in Tajikistan, particularly in the remote, mountainous areas on its western borders where central government authority is weak.
Chinese troops recently concluded a joint drill in eastern Tajikistan involving 1,200 troops from both countries.
The eight-day exercise that finished on August 13 was conducted in the autonomous Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region, a sparsely populated territory in the high Pamir mountains, which borders China’s Xinjiang region and Afghanistan.
Although this year’s exercise involved fewer troops than the 10,000 involved in a previous drill three years ago, it tested the use of advanced aerial vehicles and ground reconnaissance technology to monitor the area.
The landlocked country is strategically important for China, which is worried that the porous borders will serve as an entry point for drugs and Islamic militants into Xinjiang, where its deradicalisation strategy has led to the detention of a million Muslim minorities in reeducation camps.
It also sits along the trade routes China hopes to develop under the Belt and Road Initiative – Beijing’s flagship plan to expand its global influence through infrastructure, trade and investment – but the area has long been plagued by lawlessness and outbreaks of violence.
Artyom Lukin, a professor of international politics at Far Eastern Federal University in Vladivostok, said Russia was not happy about the deployment of Chinese forces in Tajikistan.
“Russia has traditionally considered Central Asia, including Tajikistan, as its sphere of political-military influence,” he said.
Observers said other Central Asian republics – such as Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan – are likely to stay within Moscow’s orbit, but China is steadily building closer security ties with Tajikistan.
In February, China’s defence ministry denied that it was building a base and stationing troops in the country, but defended its closer military cooperation with Tajikistan.
China has long-standing security interests in the country and in 2016 it agreed to finance 11 border outposts and a training centre for guards along the Afghan border.
This was part of a deal Beijing made through the Quadrilateral Cooperation and Coordination Mechanism – which also involves Pakistan, Afghanistan and Tajikistan – to strengthen cooperation in combating terrorism and improving security.
China has also overtaken Russia economically, becoming the largest foreign investor in Tajikistan in 2016, accounting for 30 per cent of Tajikistan's total direct accumulated investments, state news agency Xinhua reported.
China’s direct investment in Tajikistan was worth US$95 million in 2017, according to the latest available figures. China has also grown to become the country’s third largest trading partner with bilateral trade reaching around US$1.5 billion in 2018.
A recent opinion piece published by the Russian state-owned news agency Sputnik suggested China may be “getting carried away” by its investments in the region.
The article suggested that China’s growing presence in the country could lead to a “partial loss” of Tajikistan’s sovereignty and argued that Beijing may want to take control of the border with Afghanistan.
But Lukin said even though this growing involvement may be an irritant for Russia, the strategic partnership between China and Russia will remain strong.
The two countries remain the key players in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, an economic and security alliance that includes the Central Asian republics and India and Pakistan.


China is increasing its military and economic presence in parts of central Asia that Russia has traditionally considered its sphere of influence – a development some analysts believe could cause concern in Moscow.
While Russia’s influence remains strong in many former Soviet republics, China is steadily building up its military and economic influence in Tajikistan, particularly in the remote, mountainous areas on its western borders where central government authority is weak.
Chinese troops recently concluded a joint drill in eastern Tajikistan involving 1,200 troops from both countries.
The eight-day exercise that finished on August 13 was conducted in the autonomous Gorno-Badakhshan autonomous region, a sparsely populated territory in the high Pamir mountains, which borders China’s Xinjiang region and Afghanistan.
Although this year’s exercise involved fewer troops than the 10,000 involved in a previous drill three years ago, it tested the use of advanced aerial vehicles and ground reconnaissance technology to monitor the area.
The landlocked country is strategically important for China, which is worried that the porous borders will serve as an entry point for drugs and Islamic militants into Xinjiang, where its deradicalisation strategy has led to the detention of a million Muslim minorities in reeducation camps.
It also sits along the trade routes China hopes to develop under the Belt and Road Initiative – Beijing’s flagship plan to expand its global influence through infrastructure, trade and investment – but the area has long been plagued by lawlessness and outbreaks of violence.
Artyom Lukin, a professor of international politics at Far Eastern Federal University in Vladivostok, said Russia was not happy about the deployment of Chinese forces in Tajikistan.
“Russia has traditionally considered Central Asia, including Tajikistan, as its sphere of political-military influence,” he said.
Observers said other Central Asian republics – such as Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan – are likely to stay within Moscow’s orbit, but China is steadily building closer security ties with Tajikistan.
In February, China’s defence ministry denied that it was building a base and stationing troops in the country, but defended its closer military cooperation with Tajikistan.
China has long-standing security interests in the country and in 2016 it agreed to finance 11 border outposts and a training centre for guards along the Afghan border.
This was part of a deal Beijing made through the Quadrilateral Cooperation and Coordination Mechanism – which also involves Pakistan, Afghanistan and Tajikistan – to strengthen cooperation in combating terrorism and improving security.
China has also overtaken Russia economically, becoming the largest foreign investor in Tajikistan in 2016, accounting for 30 per cent of Tajikistan's total direct accumulated investments, state news agency Xinhua reported.
China’s direct investment in Tajikistan was worth US$95 million in 2017, according to the latest available figures. China has also grown to become the country’s third largest trading partner with bilateral trade reaching around US$1.5 billion in 2018.
A recent opinion piece published by the Russian state-owned news agency Sputnik suggested China may be “getting carried away” by its investments in the region.
The article suggested that China’s growing presence in the country could lead to a “partial loss” of Tajikistan’s sovereignty and argued that Beijing may want to take control of the border with Afghanistan.
But Lukin said even though this growing involvement may be an irritant for Russia, the strategic partnership between China and Russia will remain strong.
The two countries remain the key players in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, an economic and security alliance that includes the Central Asian republics and India and Pakistan.
Lukin said: “Moscow no doubt understands that in terms of security, Tajikistan’s border, adjacent to China’s Xinjiang and Afghanistan, is truly a vital concern for Beijing.
“The presence of Chinese troops could actually benefit Russia, because it will be China bearing the costs of policing Tajikistan’s mountainous border areas.”
Stephen Blank, a former professor at the US Army War College and a specialist in Eurasian security, said that while Russia has mostly stayed silent about China’s presence in Tajikistan, it was closely watching the situation.
“What happens in the long run depends on how far China goes to extend its military presence in Central Asia. And if it keeps extending, it may well provoke some expression of concern in Russia beyond the silence that has hitherto been the case,” Blank said.






